By Josiah Hsiung, Principal, NightDragon and Alec Kiang, Associate, NightDragon
Forward
We live at the turning point of an age in cybersecurity, where both the threats and the innovation economy are driven by artificial intelligence (AI). It’s been hard to miss the exciting headlines around ChatGPT and other technologies that put the power of AI into the hands of the average consumer, but this is just the tip of the iceberg when it comes to the potential this technology can have to underpin our technologies and strengthen our defenses across the digital front lines.
We already see many of these new capabilities turning artificial intelligence into action. AI already has revolutionary applications within cybersecurity and national security around supply chain, physical security, data access, threat detection and response, cloud security, and more. This is just the beginning. We expect generative AI and other types of AI to advance these action-based use cases further and drive new potential for cybersecurity, both in terms of capability and in terms of expanded market opportunity.
At NightDragon, we are closely watching this new age of AI emerge. This isn’t the creation of a new category, but rather the creation of a new foundation that will infuse its capabilities within every area of the cybersecurity, safety, security, and privacy (CSSP) sector. In a few years, we expect AI to be a foundational technology to most – if not all – of the innovations that we rely on to defend our individuals, organizations, and governments from both cyber and physical attacks.
In this multi-part report, the NightDragon team and our Advisors will thoroughly examine the new frontier of innovation created by AI, both in terms of what it means for the expansion of attacker capabilities and the potential for new technology and greater defense capabilities than ever before. For investors, this is an exciting inflection point for a new wave of opportunity, the beginning of which we have only just begun to scratch the surface. We look forward to continuing to engage and drive the market forward around AI as we work to secure our world for tomorrow.
Dave DeWalt, Founder and CEO, NightDragon
The New AI Frontier of Cybersecurity
Over the past few months, artificial intelligence (AI) has captured not only the imagination of individuals but also shown its true potential to revolutionize how we can defend today’s organizations against cyberattacks. The result is an innovation arms race, both by startups and some of the world’s largest tech organizations, to capture this new market potential and close the gap between offense and defense for today’s greatest digital threats.
As one example of this, with more than 1.8 billion visitors per month, Open AI’s ChatGPT’s rise to prominence has triggered a new global race in AI development which has led large tech firms to fast-track as many of their own AI projects in efforts to gain a market leading position in the artificial intelligence arms race. The race in AI has further extended to global enterprises, who are working quickly to integrate AI into their own solutions today by implementing Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4 or developing their own LLMs / implementing generative AI.
This is just one example of the rapid pace of innovation and evolution in the sector. The overall performance of AI systems during the last ten years has doubled approximately every six months – significantly outperforming Moore’s Law (the number of transistors on a microchip doubles every two years).
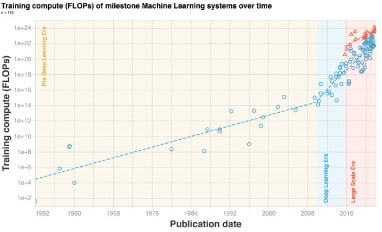
The result: AI has quickly become a strategic imperative that enterprises must implement to maintain a competitive edge. It has driven a significant AI market opportunity of nearly $200 billion in 2023 that is only expected to quadruple over the next 5+ years and disrupt numerous verticals through rapid innovation, including finance, energy, infrastructure, healthcare, retail, transportation, manufacturing, travel, agriculture and more.
In this blog series, we will explore in detail how AI is changing the risk landscape facing enterprises today, as well as the innovation and potential for where it could go in the future. These insights are informed by interviews and conversations with the NightDragon Advisor Council, which includes leading CISOs, CIOs and other executive leaders across cybersecurity and technology. The result is insights into one of the greatest opportunities in the history of technology, as well as an innovation arms race that mission-driven organizations have a responsibility to win.
Current Uses of AI in Cybersecurity
In the cybersecurity industry, AI presents a significant opportunity to enhance defensive solutions and bridge the gap between offense/defense through:
- Processing Massive Datasets: Synthesizing raw telemetry and conversion to structure data
- Providing Intelligence at Scale: Improved threat detection by implementing models that are trained on real-time data
- Improving Accuracy + Automation: Reducing false positives allowing human experts to focus on critical tasks and reduce alert fatigue
- Contextual Analytics: Identify key areas of risk across end customers’ asset base
Cybersecurity vendors utilize varied approaches to their implementation of LLMs. For example, Microsoft is leveraging its partnership with OpenAI to create Microsoft Security Copilot and Mandiant is leveraging Google’s Bard to bring AI-powered security analysis that empower security analysts with tools that accelerates the incident response, threat detection and hunting, and security reporting processes. Alternatively, other cybersecurity vendors like Palo Alto Networks, have opted to develop their own internal generative AI models (XSIAM) to empower SOC organizations with artificial intelligence. With the near-term commercial launch of these products and many others in other industries, there is significant risk in utilizing both custom-built and ready-to-use AI products. Other cyber vendors who are currently working on implementing AI to their solutions today include: Cisco, CrowdStrike, SentinelOne, among others. AI has the promise of bringing automation and simplicity to the modern cybersecurity industry, which has historically been plagued by highly fragmented and complex technologies without the talent to operate them.
Furthermore, OpenAI and Google both have created initiatives to help fund the development of growth of AI-powered defensive solutions to help bridge the gap between offense/defense. You can learn more about their initiatives here:
- OpenAI launches $1M Cybersecurity Grant Program to boost AI-powered cybersecurity capabilities and cybersecurity discourse
- Google provided Technical University of Munich’s Foundation with a $1.2M grant for scientific research in the areas of privacy, safety, and security
A New AI Risk Landscape
In his recent testimony to the Senate subcommittee hearing in May 2023, OpenAI CEO Sam Altman captured the need for innovation and proactive AI action well in saying: “If this technology goes wrong, it can go quite wrong.” This is where action by government and private organizations will come into play, as well as innovation and investment from the startup and venture capital community.
The scope of what security teams must secure has grown by a large step function since the release of OpenAI to the public and will continue to do so as additional advancements are made around artificial intelligence. AI / ML development teams, in coordination with security teams, must adopt rigorous processes, checks and balances to ensure the integrity and safety of AI models from development through deployment.
“The more AI models are used for interesting and sophisticated tasks and automation, there will be an increase in incentives for nation states to conduct targeted cyber attacks to compromise these AI models” – Christoph Peylo, Chief Cyber Security Officer at Bosch
Attacks against AI models differ from traditional cybersecurity attacks (e.g. malware) as vulnerabilities in AI do not necessarily require “hacking” of systems but rather instead can come from model exploitations (e.g. model inference and evasion, see below for an overview of both kinds of attacks). If AI models are compromised, there is a significant risk of intellectual property theft, financial harm, identity theft, fraud, and potential reputational damages.
According to a survey conducted by DataRobot in 2022, more than 1 in 3 organizations surveyed (n=365) have experienced challenges or direct business impact due to an occurrence of AI bias in their algorithms. Adding to this challenge is the fact that transparency in AI models is often limited. “Black box” AI models can be so complex that individuals may struggle to comprehend and thoroughly evaluate them, despite their ability to generate accurate results. Companies need to balance the urgency of deploying artificial intelligence with the need to produce safe AI solutions.
Attackers and adversaries are also innovating their tactics, techniques, and procedures, both in how they are leveraging AI themselves or in how they can compromise its models. The MITRE ATLAS framework lists 60+ known malicious tactics and techniques that can compromise an ML model across the production lifecycle – and the list has continued to grow. With ML tools like ChatGPT achieving unprecedented adoption rates (1 million users in 5 days vs. some of the top social media websites that took months to achieve 1 million users), organizations must act quickly to take preventative measures and ensure the security and safety of this technology.
Based on our discussions with our Advisor Council, we have identified 4 common risks that are impacting enterprises today that will inform the opportunity for innovators in this sector:
- Data Poisoning:
Adversaries manipulate the model by inserting malicious data into the training data set. These instances contain subtle modifications in the training data that aim to deceive the model during the training process. The goal is to influence the model’s learned decision process by introducing bias or causing the model to make incorrect predictions on specific inputs (backdooring).
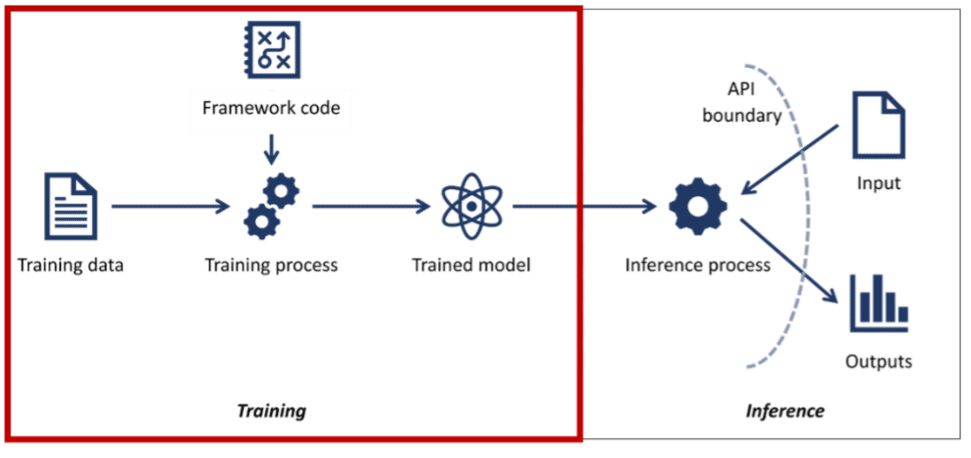
As an example, adversaries leveraged Google’s Gmail spam filters by flooding the system with millions of emails, causing the classifier algorithms to become perplexed. Adversaries generated many adversarial examples that were then used to retrain the model with poisoned emails – which altered the behavior of the spam filter. Through this method, attackers managed to successfully send numerous malicious emails bypassing Google’s detection.
- Model Evasion:
Adversaries query the model with manipulated inputs with the goal of getting the desired output. Often times, manipulated inputs may be imperceptible to the human eye but are designed to exploit weaknesses in the model’s underlying algorithms. The consequences of model evasion attacks can lead to incorrect predictions, compromise the integrity of decision-making systems, and potentially allow threat actors to manipulate the model’s outputs for their benefit.

In the image above, the stop sign image has been slightly augmented to the point where the machine can no longer classify the image as a stop sign. This can have significant implications, especially in a situation where autonomous vehicles are not able to accurately identify stop signs.
- Model Inference:
Adversaries query the black box model and observe the output response in an attempt to infer the training data. The attacker typically needs to query the target model with a considerable number of tries to build its own variation of a model training set – following which, the compromised data can be utilized to build an approximated version of the original model (model extraction).
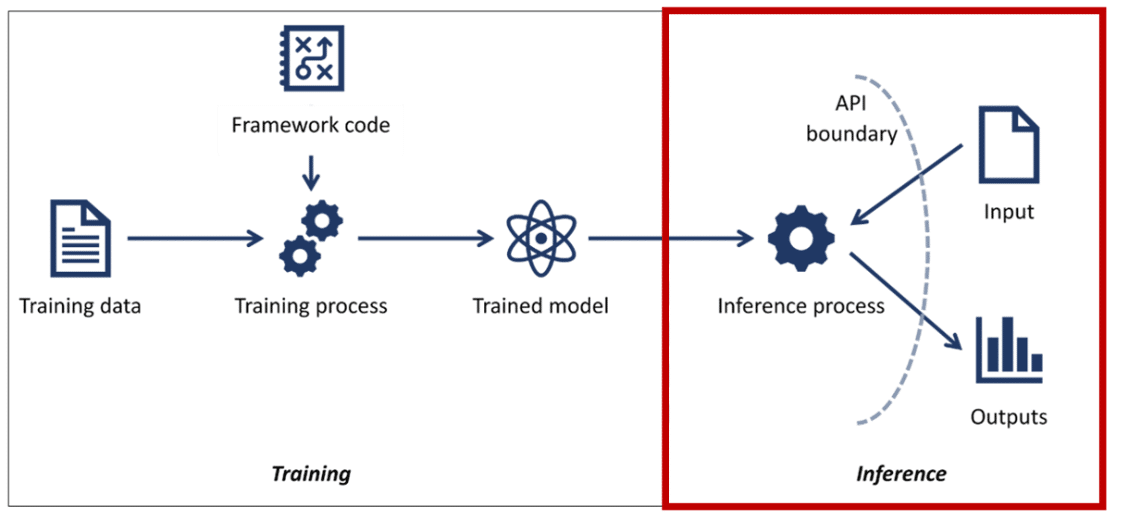
- Model Extraction:
Replicating a target ML model without having direct access to the model’s parameters or training data. Functional extraction utilizes queries and responses collected through interactions with the target model to build a copy that can approximate the original model. Bosch AIShield conducted an ethical hacking case where researchers extracted a pedestrian detection algorithm developed over 10 months within 4 hours and only 4% delta to the original model accuracy. If this type of attack were enacted in real-life, data extraction can result in significant financial losses and loss of IP.

Closing Thoughts
The rapid rise of artificial intelligence has ushered in a new frontier of opportunities and challenges. As AI continues to become a strategic imperative for enterprises seeking to maintain their competitive edge, there will be new risks and challenges to consider. Attacks against AI models differ from traditional cybersecurity attacks, and vulnerabilities in AI can lead to intellectual property theft, financial harm, identity theft, and reputational damages. The importance of securing AI models and addressing risks cannot be overstated.
Organizations must maintain responsible AI practices and secure their AI-related assets – so that they can ultimately harness the full potential of AI’s benefits while mitigating potential harm. In our following blog, we will explore the new wave of AI security innovation and regulations that respond to the risk associated with implementing AI.
NightDragon is committed to staying at the forefront of the AI security landscape, supporting and collaborating with founders developing cutting-edge security solutions to safeguard against adversarial ML threats. If you’re a founder in the AI security space, we’d love to hear from you!
Please keep an eye out next week for Part 2 of our AI blog series, discussing the AI innovation landscape to combat the threats described above. Keep an eye on our blog page for future iterations.

